Quadriceps Strain Rehab Exercises: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover a detailed, evidence-based recovery plan! Download our step-by-step quad strain rehab exercises PDF, crafted by a Doctor of Physical Therapy, for optimal healing.
This guide offers a comprehensive, home-based routine, simplifying your journey back to full function and preventing re-injury through progressive phases.
Understanding Quadriceps Strains
Quadriceps strains, common injuries, involve damage to the muscles at the front of the thigh – rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. These injuries range from mild (Grade I) with minor fiber tears, to moderate (Grade II) with more significant damage, to severe (Grade III) involving complete muscle rupture.
Understanding the severity is crucial for guiding rehabilitation. Pain, swelling, and difficulty with activities like walking, squatting, or kicking are typical symptoms. A proper diagnosis, often involving a physical examination, is essential before starting any quad strain rehab exercises PDF program.
The quadriceps muscle group plays a vital role in knee extension and hip flexion (rectus femoris). Strain occurs due to sudden contractions, overstretching, or direct impact. Effective rehabilitation focuses on reducing inflammation, restoring range of motion, strengthening the muscles, and regaining functional abilities. A progressive approach, as detailed in a comprehensive rehab protocol, is key to a successful recovery.

Phase I: Acute Phase (First 24-48 Hours)
Initial management, within the first 24-48 hours, centers on minimizing inflammation and pain. The RICE protocol – Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation – is paramount. Rest involves avoiding activities that aggravate the injury. Apply ice packs for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours. Compression, using an elastic bandage, helps reduce swelling, and elevation above the heart promotes fluid drainage.
A quad strain rehab exercises PDF for this phase will emphasize gentle interventions. Avoid aggressive stretching or strengthening. Focus on pain control and protecting the injured tissue. Early, pain-free range of motion exercises, like gentle knee bends, prevent stiffness.
Limiting muscle atrophy is also important. Begin with isometric quadriceps sets – tightening the thigh muscles without moving the knee – to activate the muscles without stressing the strain. This early activation helps maintain some muscle mass during the initial healing phase.
RICE Protocol Implementation
Rest is crucial; discontinue activities causing pain. Ice application, for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours, reduces inflammation and pain – always use a barrier to protect the skin. Compression, achieved with an elastic bandage, minimizes swelling, but avoid overly tight wrapping which could impede circulation. A quad strain rehab exercises PDF will detail proper bandage technique.
Elevation, positioning the leg above heart level, facilitates fluid drainage and reduces edema. Combine these elements consistently for optimal results. The initial 24-48 hours demand strict adherence to RICE.
Monitor for increased pain, numbness, or changes in skin color, indicating potential complications. A downloadable PDF resource will visually demonstrate correct RICE application. Remember, RICE isn’t a cure, but a vital first step in managing a quadriceps strain and preparing for subsequent rehabilitation phases.
Range of Motion Exercises – Gentle Movements

Initiate gentle range of motion (ROM) exercises within pain-free limits to prevent stiffness and maintain joint mobility. A quad strain rehab exercises PDF will illustrate these movements. Begin with heel slides, slowly bending and straightening the knee while lying down. Ankle pumps – pointing and flexing the foot – improve circulation and reduce swelling.
Perform gentle knee extensions, focusing on controlled movement, avoiding forceful contractions. These exercises should be pain-free; stop immediately if discomfort arises. Aim for 10-15 repetitions, several times a day.
Gradually increase the range of motion as tolerated, but never push beyond your pain threshold. Consistent, gentle ROM exercises are fundamental to restoring function and preparing the quadriceps for strengthening. A visual guide within the PDF will ensure correct form and technique.
Limiting Muscle Atrophy – Early Activation
Early quadriceps activation is crucial to minimize muscle atrophy following a strain, detailed within a quad strain rehab exercises PDF. Begin with quad sets – tightening the thigh muscles while keeping the leg straight, holding for 5-10 seconds, and repeating 10-15 times. This isometric contraction helps maintain muscle mass without stressing the injured tissue.
Another effective exercise involves gently contracting the quadriceps while performing heel slides. This combines ROM with muscle activation. Ankle pumps, as previously mentioned, also contribute to circulation and reduce swelling, indirectly supporting muscle health.
These early activation exercises should be performed frequently throughout the day, focusing on controlled contractions and avoiding any pain. The PDF provides clear instructions and modifications to suit individual needs, preventing further injury and promoting faster recovery.
Phase II: Early Strengthening (Flexibility Improving)

As flexibility improves, a quad strain rehab exercises PDF guides you into Phase II, focusing on gentle strengthening. Isometric exercises, like quad sets with a towel under the knee, continue to build strength without joint movement. Progress to isotonic exercises – controlled knee extensions and hamstring curls – using light resistance or bodyweight.
Electrical stimulation (e-stim) can be incorporated to re-educate the quadriceps muscle, enhancing activation and reducing atrophy. Low-impact cardio, such as stationary cycling or walking, improves circulation and overall conditioning, preparing the leg for more demanding exercises.
The PDF emphasizes proper form and gradual progression. Listen to your body, avoiding pain, and adjust the intensity as needed. This phase aims to restore basic strength and function, setting the foundation for advanced rehabilitation.
Isometric Exercises for Quadriceps
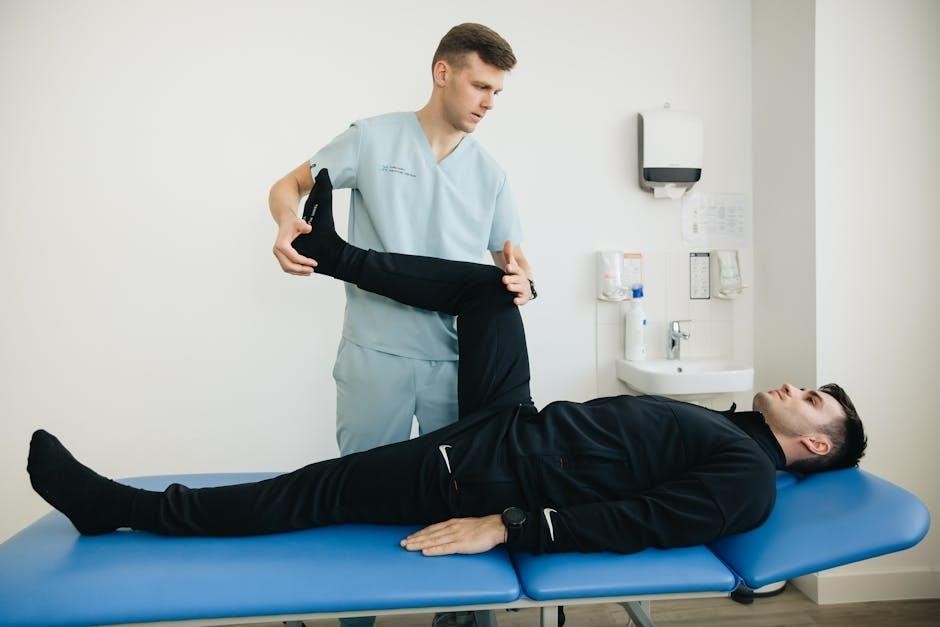
A detailed quad strain rehab exercises PDF highlights isometric exercises as crucial for early strengthening. These involve contracting the quadriceps muscle without changing its length, minimizing stress on the healing tissue. A key exercise is the “quad set”: lie on your back with a rolled towel under the knee.
Focus on tightening the thigh muscles, pressing the back of the knee firmly into the towel. Hold for 5-10 seconds, then relax. Repeat 10-15 times, performing 2-3 sets. Another variation is terminal knee extensions – actively contracting the quadriceps to straighten the knee while keeping the heel on the surface.
The PDF stresses maintaining proper form and avoiding any pain during these exercises. Isometric contractions help maintain muscle activation and prevent further atrophy during the initial stages of recovery, preparing the muscle for more dynamic movements.
Isotonic Exercises – Controlled Movements
A comprehensive quad strain rehab exercises PDF details isotonic exercises as the next step after isometric training. These involve muscle contractions with a change in muscle length, introducing controlled movement. Short arc quads are frequently recommended: seated with a slight bend in the knee, slowly straighten the leg, then lower it back down.
The PDF emphasizes performing these exercises slowly and deliberately, focusing on controlled motion rather than speed; Leg extensions with light resistance (ankle weights or resistance bands) are also included, starting with minimal weight and gradually increasing it as strength improves.
Wall squats, performed to a shallow angle, are another beneficial isotonic exercise. The document stresses avoiding deep squats initially to prevent re-injury. Proper form and pain-free movement are paramount throughout this phase, as outlined in the PDF.
Electrical Stimulation – Muscle Re-education
A detailed quad strain rehab exercises PDF explains that electrical stimulation (e-stim) aids muscle re-education, particularly when voluntary contraction is difficult post-injury. It utilizes low-intensity electrical currents to stimulate the quadriceps muscle, helping to restore neuromuscular control.
The PDF clarifies that e-stim doesn’t replace active exercise but complements it. It’s often used to reduce muscle inhibition and improve the muscle’s ability to contract efficiently. Different waveforms and parameters are employed based on the stage of recovery, as detailed within the PDF’s protocols.
Typically, electrodes are placed on the quadriceps muscle belly, and the stimulation is applied during or before active exercises. The document emphasizes the importance of professional guidance to ensure correct electrode placement and parameter settings, maximizing benefits and minimizing risks.
Conditioning Exercises – Low Impact Cardio
A comprehensive quad strain rehab exercises PDF highlights the crucial role of low-impact cardiovascular conditioning in maintaining overall fitness during recovery. It emphasizes avoiding activities that exacerbate pain or stress the injured quadriceps, while still promoting cardiovascular health.
The PDF recommends options like stationary cycling (with minimal resistance), elliptical training, and swimming as excellent choices. These activities allow for controlled movement and reduced impact on the knee joint. Gradual increases in duration and intensity are key, guided by pain levels.
The document stresses the importance of monitoring for any signs of increased pain or swelling. It advises against pushing through discomfort, as this could hinder the healing process. The PDF provides specific guidelines on duration and frequency, tailored to each phase of rehabilitation.
Phase III: Intermediate Strengthening
A detailed quad strain rehab exercises PDF outlines Phase III as a pivotal stage, focusing on building strength and preparing the quadriceps for more demanding activities. This phase transitions from basic muscle activation to more challenging exercises, progressively increasing the load on the recovering muscle.
The PDF details the introduction of isokinetic exercises, utilizing specialized equipment to control the speed of movement, and progressive resistance training with weights or resistance bands. Emphasis is placed on proper form and controlled execution to prevent re-injury.
The document stresses the importance of pain monitoring throughout this phase. Any increase in pain signals the need to reduce intensity or modify the exercise. The PDF provides specific sets, reps, and resistance levels, tailored to individual progress and injury severity.
Isokinetic Exercises – Variable Speed Training
A comprehensive quad strain rehab exercises PDF details isokinetic training as a crucial component of Phase III, utilizing specialized equipment to deliver consistent resistance throughout the full range of motion. Unlike traditional weightlifting, isokinetic exercises control the speed of contraction, allowing for targeted muscle strengthening.
The PDF explains how this method minimizes the risk of re-injury by accommodating the patient’s evolving strength levels. Exercises typically involve knee extension and flexion at varying speeds, challenging the quadriceps in a controlled manner. The document provides specific protocols, including target speeds and repetition schemes.
Proper setup and technique are emphasized within the PDF, alongside guidance on monitoring for pain or discomfort. Isokinetic training aims to restore optimal muscle function and prepare the leg for more functional movements.
Progressive Resistance Training – Increasing Load
A detailed quad strain rehab exercises PDF outlines progressive resistance training as a cornerstone of Phase III recovery. This involves gradually increasing the weight or resistance used during exercises, challenging the quadriceps to adapt and grow stronger. The PDF emphasizes a systematic approach, starting with lighter weights and incrementally increasing the load as strength improves.
Common exercises detailed include leg presses, squats, and lunges, with specific recommendations for sets, repetitions, and weight selection. The document stresses the importance of maintaining proper form throughout each exercise to prevent re-injury; It also highlights the need to listen to your body and avoid pushing through pain.
The PDF provides clear guidelines on when and how to increase resistance, ensuring a safe and effective progression towards full strength restoration.
Phase IV: Advanced Strengthening & Functional Exercises
A comprehensive quad strain rehab exercises PDF details Phase IV as a critical stage focusing on restoring full function. This phase introduces advanced exercises designed to mimic real-life movements and prepare the athlete for return to activity. Eccentric exercises, like controlled leg extensions, are emphasized to build strength and control during muscle lengthening – vital for injury prevention.
Proprioceptive training, utilizing balance boards or unstable surfaces, is also highlighted to improve balance and coordination. The PDF outlines functional movements, such as agility drills and plyometrics, progressively increasing in intensity.
The document stresses the importance of proper form and controlled movements throughout this phase. It provides specific guidelines for exercise selection, progression, and monitoring for any signs of re-injury, ensuring a safe and effective transition back to sport-specific activities.
Eccentric Exercises – Focus on Muscle Control
A detailed quad strain rehab exercises PDF emphasizes eccentric training as pivotal for rebuilding quadriceps strength and preventing re-injury. Eccentric exercises focus on lengthening the muscle under load, crucial for controlling deceleration and absorbing impact forces during activity.
The PDF outlines specific exercises like slow, controlled leg extensions, emphasizing a 3-5 second lowering phase. Step-downs from a platform and single-leg squats are also included, progressing in difficulty. Proper form is paramount; maintaining a neutral spine and controlled movement throughout each repetition is stressed.
The document highlights the importance of starting with lighter resistance and gradually increasing the load as strength improves. It also advises monitoring for delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS) and adjusting the intensity accordingly, ensuring optimal muscle adaptation and minimizing the risk of further strain.
Proprioceptive Training – Balance & Coordination

A comprehensive quad strain rehab exercises PDF underscores the vital role of proprioceptive training in restoring full function after injury. Proprioception, your body’s awareness of its position in space, is often compromised following a quadriceps strain, impacting balance and coordination.

The PDF details exercises like single-leg stance, progressing from stable to unstable surfaces (foam pad, wobble board). Dynamic balance drills, such as reaching in various directions while maintaining single-leg balance, are also included. These exercises challenge the neuromuscular system to regain control and stability.
The document stresses the importance of performing these exercises slowly and deliberately, focusing on maintaining proper alignment and preventing compensatory movements. Gradual progression is key, increasing the difficulty as balance and coordination improve, ultimately preparing the athlete for return to activity.
Functional Movements – Simulating Activities
A detailed quad strain rehab exercises PDF emphasizes bridging the gap between controlled exercises and real-world activities. This phase focuses on functional movements, mimicking the demands of the athlete’s specific sport or daily life, ensuring a safe return.
The PDF outlines exercises like controlled squats, lunges (forward, lateral, reverse), and step-ups, gradually increasing the range of motion and load. Agility drills, such as cone drills and shuttle runs, are incorporated to improve dynamic movement patterns and reaction time.
The document highlights the importance of proper form and technique throughout these exercises, preventing re-injury. It advises starting with simpler movements and progressively increasing complexity, mirroring the athlete’s activity level. Monitoring for pain or discomfort is crucial, adjusting the program as needed.
Phase V: Return to Activity
A comprehensive quad strain rehab exercises PDF details a cautious return to activity, emphasizing a gradual reintegration into sport-specific training. This phase isn’t about pushing limits, but carefully monitoring the body’s response to increasing demands.
The PDF stresses sport-specific drills, progressively increasing intensity and duration. For example, a runner might start with jogging, then interval training, and finally full-speed runs. It highlights the importance of warm-up and cool-down routines before and after each session.
Crucially, the document emphasizes continuous monitoring for re-injury. Pain, swelling, or decreased function are red flags, signaling a need to reduce activity. Long-term prevention strategies, including consistent strengthening and flexibility exercises, are also detailed within the PDF.
Sport-Specific Training – Gradual Reintegration
The quad strain rehab exercises PDF meticulously outlines a phased approach to sport-specific training. Initial drills mimic movements required in your activity, starting at low intensity and short duration. For instance, basketball players begin with shooting drills, avoiding explosive jumping.
Progression is key, detailed within the PDF, increasing speed, power, and complexity gradually. A runner might transition from jogging to strides, then to interval training, always monitoring for pain. The document emphasizes avoiding sudden increases in workload.
The PDF stresses the importance of replicating game-like scenarios, but with controlled parameters. This allows the quadriceps to adapt to the demands of the sport without risking re-injury. Proper technique and form are paramount throughout this reintegration process.
Monitoring for Re-Injury – Pain & Function Assessment
The quad strain rehab exercises PDF highlights diligent self-monitoring as crucial during the late stages of recovery. Regularly assess pain levels – at rest, during activity, and post-exercise – using a standardized scale. Any increase in pain signals a need to reduce intensity or regress to a previous phase.
Functional assessments, detailed in the PDF, evaluate your ability to perform sport-specific movements. These include hopping, agility drills, and sprinting, comparing performance to your uninjured leg. Documenting these assessments provides objective data to track progress.
The PDF emphasizes listening to your body and avoiding the “no pain, no gain” mentality. Consistent monitoring, combined with objective functional testing, minimizes the risk of re-injury and ensures a safe return to activity. Seek professional guidance if concerns arise.

Long-Term Prevention Strategies – Warm-up & Cool-down

The quad strain rehab exercises PDF underscores that preventing recurrence requires consistent implementation of warm-up and cool-down routines. A dynamic warm-up, detailed within the PDF, prepares muscles for activity with movements like leg swings and walking lunges, increasing blood flow and flexibility.
Prioritize quadriceps-specific stretches during your warm-up, holding each stretch for 30 seconds. Following activity, a cool-down incorporating static stretching – holding stretches without movement – helps reduce muscle soreness and improve flexibility.
The PDF also recommends incorporating regular strength training to maintain quadriceps strength and endurance. Consistent adherence to these strategies, as outlined in the guide, significantly reduces the risk of future quadriceps strains and promotes long-term athletic performance.
